When it comes to protecting your home from power outages choosing the right backup power solution is essential. The world of home power backup presents a range of decisions, each with its own significance. Selecting the wrong system could mean living with suboptimal results during critical moments.
But how do you make the right choice? Have you considered every factor that could impact your decision? What are the key differences between a generator and a battery backup system? And perhaps more importantly, what do you not yet know that might sway your decision?
In this post, we’ll guide you through a comprehensive breakdown of both options, giving you the knowledge to confidently choose the solution that fits your specific needs and ensures your home stays powered through any outage. You may even choose a combination of both the generator and battery backup for the most complete form of energy security.
Why Do You Need Backup Power?
Aside from the obvious benefits like ensuring power for medical devices, home security, and comfort, there are several other important reasons for having backup power, especially in areas prone to outages:
- Protecting Perishable Goods: In the event of an outage, refrigerators and freezers can lose power, leading to food spoilage within hours (FDA ).
- Work-from-Home Reliability: With more people working remotely, a stable power supply is critical.
- Weather-Related Disasters: Power outages often occur during severe weather events, making it important to maintain communication when you need it most.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing your home is prepared for an outage—whether it lasts for hours or days—provides peace of mind.
- Energy Independence: If you’re using solar + battery backup, you’re reducing your reliance on the grid, which can protect you from utility rate hikes or grid failures.
- Maintaining Water Supply: If your home relies on well water, a backup power system can keep your water pump running during outages( Energy Sage).
- Preserving Comfort and Safety in Extreme Weather: During hot summers or freezing winters, losing power can mean losing your HVAC system.
- Supporting Critical Household Systems: Systems like sump pumps, which protect your home from flooding, require power.
In summary, backup power provides not just convenience but also security, safety, and independence in a range of situations. It’s a worthwhile investment for anyone who wants to ensure their home remains operational and comfortable during outages, no matter the reason.
Generators and How They Work
A generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, typically through the process of electromagnetic induction. For over half a century, generators have been widely used to provide essential backup power during outages, ensuring that homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure remain operational when the primary electrical grid fails. Their reliability has made them a cornerstone in emergency preparedness and power resilience across various sectors.
However, the key factor to remember is that generators rely on fuel—be it gasoline, diesel, propane, or natural gas—to function. While they can produce electricity continuously as long as fuel is available, this dependence poses a critical challenge: what happens when the fuel supply is interrupted? Without fuel, a generator becomes ineffective, leaving homes and businesses vulnerable to extended power outages. Regular maintenance and proper fuel storage are necessary, but fuel scarcity can complicate long-term reliance on generators (Generators | HowStuffWorks).
Below are the pros and cons of using a generator and home battery backup.
Generator Pros:
- Lower Upfront Cost: A generator typically costs less to purchase and install compared to a battery backup system, making it an accessible option for homeowners needing backup power.
- Readily Available Fuel: Generators powered by natural gas can be directly connected to a home’s natural gas line, offering a steady fuel source without the need for refueling.
Generator Cons:
- Fuel Dependency: Generators rely on fuel to run, which can become a problem during severe weather events when fuel is scarce. For gasoline and diesel models, you need to store fuel safely, which can be hazardous and impractical for long-term use.
- No Federal Incentives: Unlike clean energy solutions, generators do not qualify for the 30% federal tax credit due to their reliance on fossil fuels. This absence of incentives makes them less financially appealing compared to renewable energy systems, which benefit from government support aimed at promoting sustainability.
- Rising Fuel Costs: Fossil fuels are expected to become increasingly expensive in the coming years, making fuel reliance a potential vulnerability. Over time, this could result in higher costs compared to the long-term savings of a battery backup system, which leverages renewable energy.
- Maintenance: Generators require regular maintenance, including oil changes, fuel checks, and running the system periodically to ensure function. The average cost of maintenance a year can be from $400 to $650.
- Emissions: Generators produce carbon monoxide, contributing to air pollution. They must be installed outdoors and away from windows to avoid dangerous fumes. This makes them less environmentally friendly compared to battery systems.
- Noisy Operation: Generators are loud, which can be disruptive, particularly in residential or quiet neighborhoods. Many HOAs ban the use of generators because of noise pollution.
To summarize, generators can be a practical solution if you have consistent access to a fuel supply and prioritize a lower upfront cost over long-term savings. While they do not qualify for federal incentives aimed at promoting clean energy, they are often more accessible for immediate power needs. Generators are most suitable for those who are not concerned with noise pollution or the environmental impact, as they tend to produce emissions and operate loudly. If the ease of fuel availability and immediate, reliable backup power is your primary concern, a generator might be the more straightforward choice.
Battery Backup Systems and How They Work
Home battery backup systems have their roots in early energy storage technologies, which were primarily used in off-grid homes reliant on renewable energy sources. As solar energy began gaining popularity in the 2000s due to falling costs and government incentives, the demand for more efficient energy storage grew. The development of lithium-ion battery technology significantly boosted the efficiency, longevity, and reliability of battery storage, making it a viable option for homeowners looking to store energy from solar panels or other renewable sources.
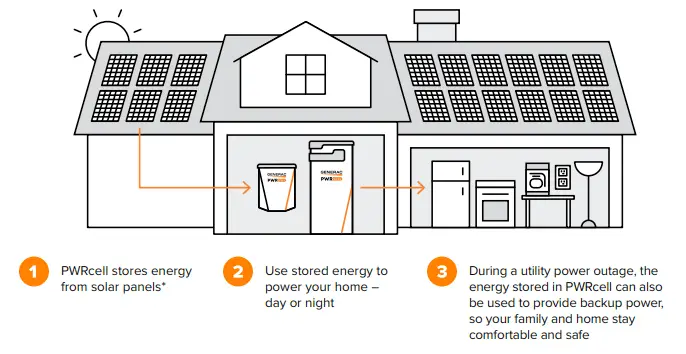
The rise in extreme weather events, increased electricity costs, and growing concerns about climate change in the 2020s have accelerated the adoption of battery backups in homes. These systems now provide a clean, reliable solution for power outages and allow homeowners to manage their energy usage more efficiently. Advances in smart technology and government incentives have also helped make battery backups a popular choice for sustainable energy storage.
Battery Backup Systems Pros:
1. Long-Term Savings: While the upfront cost of a battery backup system is higher, the long-term savings, particularly when paired with solar, can offset this. Homeowners can store excess solar power during the day and use it during peak hours or outages, reducing their reliance on the grid.
2. Instant Power: Battery systems provide seamless, instant power during an outage. There is no delay or noise when they switch on, unlike generators that can take several seconds or minutes to start.
3. Low Maintenance: Batteries require minimal maintenance compared to generators. Generators require regular servicing, including oil changes and fuel storage checks, whereas batteries typically need little more than routine inspections.
4. Incentives: Battery backup systems are often eligible for government incentives, such as the 30% federal tax credit for clean energy installations. These incentives help lower the cost of installation, making batteries a more financially viable long-term solution.
5. Quiet Operation: Unlike generators, which can be noisy, battery backup systems are silent, making them more suitable for residential areas where noise pollution could be an issue.
6. Energy Independence: Batteries allow homeowners to store excess energy and reduce reliance on the grid. This is particularly useful during blackouts or periods of high electricity demand.
7. Longer Duration with Solar: When paired with solar panels, battery systems can be recharged daily, offering extended power even through multi-day or multi-week outages. This makes them much more resilient during long-term power failures, as they don’t rely on external fuel sources like a generator.
8. Fuel Independence: Unlike generators, which require continuous fuel (gasoline, propane, diesel, or natural gas), battery backups paired with solar are fuel-independent, which means homeowners don’t have to worry about running out of fuel or accessing more during emergencies.
9. Environmentally Friendly: Battery backups are powered by renewable energy, typically from solar panels, and do not emit greenhouse gases or other harmful pollutants. This makes them a cleaner alternative to generators, which rely on fossil fuels.
Cons of Home Battery Backup:
1. Higher Upfront Costs: Battery backup systems have a higher initial installation cost compared to generators. This expense can range from $8,000 to $20,000 or more, depending on capacity and whether it’s paired with solar panels (EnergySage).
2. Needs Solar for Long-Duration Power Outages: While batteries can provide backup power for short outages, for long-duration power outages, they require solar panels to continuously recharge. Without solar, they will eventually deplete, limiting their effectiveness in extended outages.
3. Capacity Constraints: Battery backups are generally designed to power essential appliances only. To run the entire house or high-energy devices (e.g., air conditioning), multiple battery units may be required, significantly raising the cost.
To summarize, battery backup systems offer a clean, efficient, and low-maintenance solution for home power outages, particularly when paired with solar panels. These systems provide instant, seamless power, are silent, and help homeowners achieve energy independence by storing excess energy and reducing reliance on the grid. They also qualify for government incentives, such as the 30% federal tax credit. However, battery backups come with higher upfront costs, typically ranging from $8,000 to $20,000, and are generally designed to power only essential appliances unless multiple units are installed. For long-duration outages, batteries need solar to continuously recharge, limiting their effectiveness without it.
Choosing Both – Best of Both Worlds?
For homeowners in areas prone to long outages or natural disasters, combining a generator with a battery backup system might offer the most reliable solution. Here’s why:
- Seamless Transition: Battery backup systems can power critical appliances immediately when the grid fails, while a generator can kick in once the battery depletes, ensuring continuous power.
- Fuel Efficiency: Using a battery for shorter outages or to manage smaller energy loads during an outage reduces the need for constant generator use, saving fuel.
- Extended Backup Power: A battery backup paired with a generator allows you to maximize both systems. The generator can recharge the battery during long outages, providing power even if solar panels are not generating enough energy. (Battery + Generator).

In Conclusion…
Ultimately, both generators and battery backup systems offer unique benefits depending on your home’s needs and your preferences. Generators are cost-effective upfront and provide continuous power during extended outages but come with higher fuel dependency, noise, and environmental costs. On the other hand, battery backup systems, especially when paired with solar panels, offer a cleaner, quieter, and more sustainable option for powering essential appliances during outages, though they have a higher initial investment. For homeowners in areas with frequent, prolonged outages, combining a generator with a battery system could provide the best of both worlds, ensuring both continuous power and fuel efficiency. Evaluating your energy needs, outage frequency, and environmental concerns will help you determine the best option to ensure your home remains powered and secure through any situation.

